The evolution of ride-sharing service and trend ASEAN
The evolution of ride-sharing service and trend in ASEAN
With the remarkable success of UBER, the global landscape of private transportation has changed dramatically with the introduction of revolutionary business concept known as “sharing economy”. Ride-sharing, sharing economy for mobility, works on peer-to-peer, driver-partner model on the digital platform while traditional taxi business heavily invests in vehicle-related assets such as vehicles, management costs and wages, etc. Due to light-asset business model, ride-sharing service providers has been able to scale their services worldwide with less marginal cost.
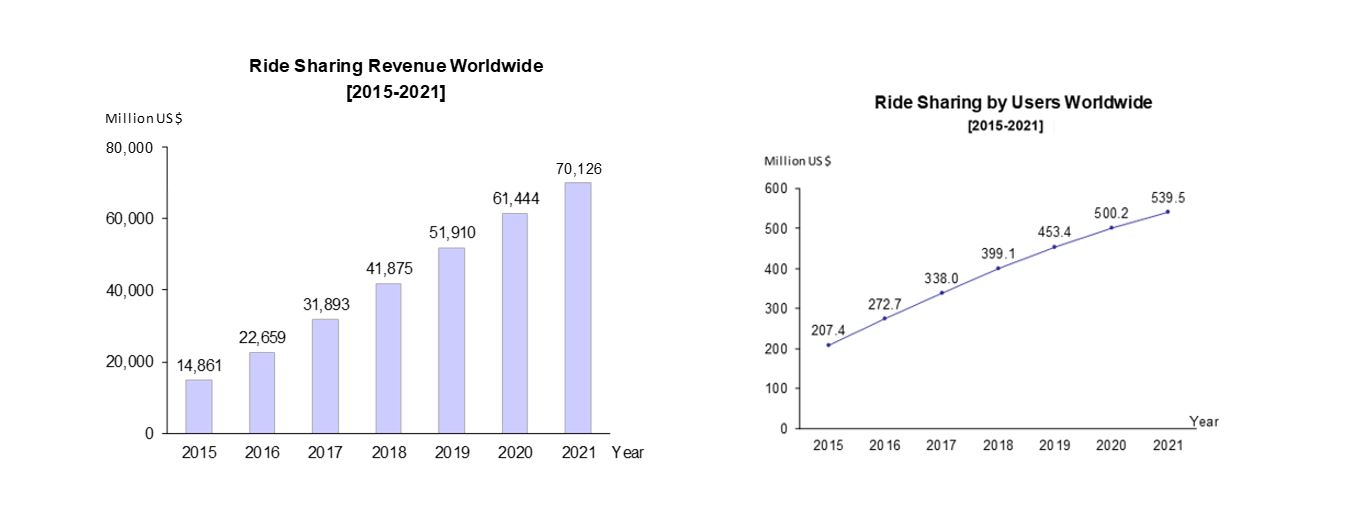
According to Statista, in 2016, the ride-sharing market value was approximately 22,659 million USD while the market growth rate between 2017 and 2021 is predicted to be 21.8% annually on average. On the other hand, the number of users has been annually increasing by 8.6% and will reach 539.5 million in 2021.
In the early stage of ride-sharing service, it was only initiated to encourage people to gain extra money from driving their personal car. However, due to an increase in market demand, new regulatory constraints and higher competitions, the ride-sharing service has become more comprehensive than the traditional method of requesting taxis, cars, motorcycles, etc. Nowadays, a ride-hailing service has become the common word for a ride-sharing service.
ASEAN Market
After the merger of UBER and Grab in March 2018, ASEAN, the world’s seventh largest economy with total GDP of 2.8 trillion USD in 2017, is becoming the interesting market for a proxy war from giant companies all over the world via remaining 2 unicorns, Grab and Go-Jek.
Grab, backed by Softbank, Toyota, Didi Chuxing and Microsoft, is the biggest service provider in ASEAN covering 235 cities in 8 counties at 14 billion USD valuation while Go-Jek, backed by Google, Tencent and JD, is operating in 50 cities 4 counties at 11 billion USD valuation. No matter how much influence from those back up companies, the proxy war is gradually becoming more comprehensive beyond transportation related service. At present, Grab is still the front-runner in most countries as the first mover in this region but Go-Jek is attempting to catch up its rival with rapid speed.
From ride-sharing to Super App
According to Fortune, both Grab and Go-Jek are aiming to become “every day super apps” that engages consumers on multiple fronts – offering food delivery, digital payments, financial services and even health care along with rides. The model is pioneered in China by Alibaba’s Alipay and Tencent’s WeChat.
Mobile Finance: GrabPay operates in 6 countries and explores the pre-paid-card partnership with Mastercard while Go-Pay is becoming the main payment method from its surrounding services such as Go-Mart (grocery shopping), Go-Clean (housecleaning), Go-Glam (hairstyling and makeovers), and Go-Massage (self-explanatory).
Mobile Health Care: Grab in August announced a joint venture with China’s Ping An Healthcare and Technology to explore delivering medical consultations via app, along with medicine delivery and appointment booking.
Mobile Miscellany: On 23 April 2019, Grab had announced to release 4 new services including Trip Planner service, Hotel service, Video service and Ticket service starting in Singapore
Not only increasing customer engagement, but every day super-apps promise a new mode of connecting with customers and an opportunity to benefit from data about their preferences and purchasing behaviour.
Autonomous car: promising innovative technology in transportation
Comparing with traditional transportation technology, the upcoming autonomous car technology has been the most famous topic in transportation because it supposes to change how people transport forever by offering a lower cost with more convenient and better travelling experience to consumers. In addition, it is going to change the competitive landscape of all transportation service completely not only ride-sharing service and automotive manufacturing.
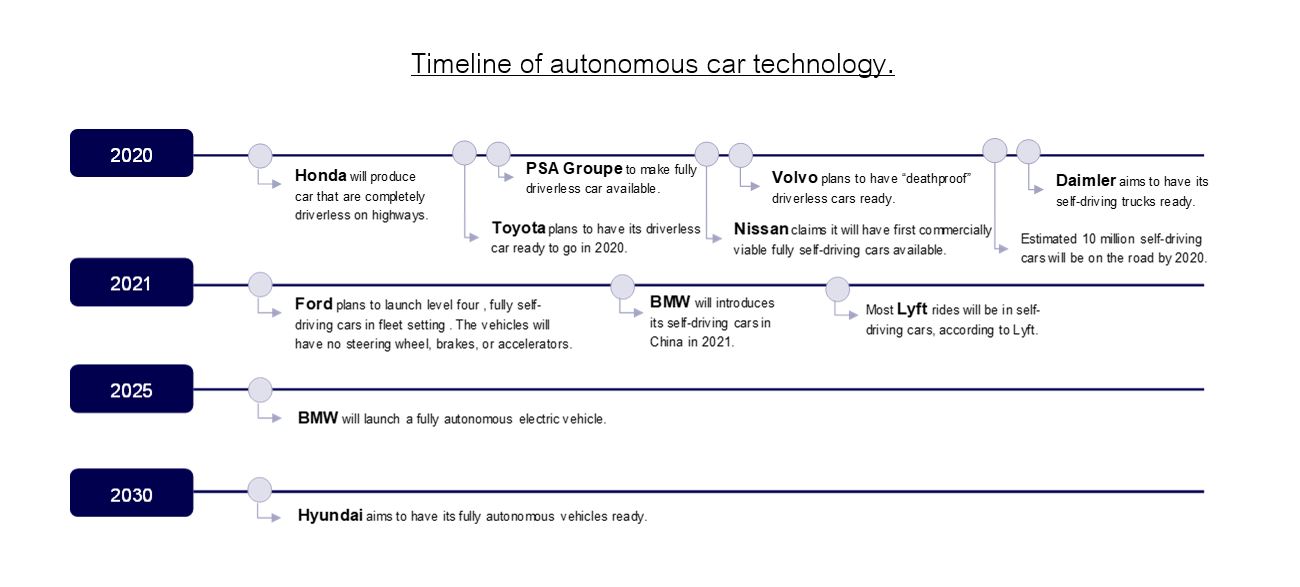
According to the timeline below, the autonomous car technology is predicted to be released for commercial in near future. Not only automotive manufacturers, but ride-sharing service providers and technology companies such as Waymo, Alphabet’s subsidiary, are also competing against each other and attempting to implement the technology into their products and services as soon as possible in order to gain the first mover advantage.
Timeline of autonomous car technology
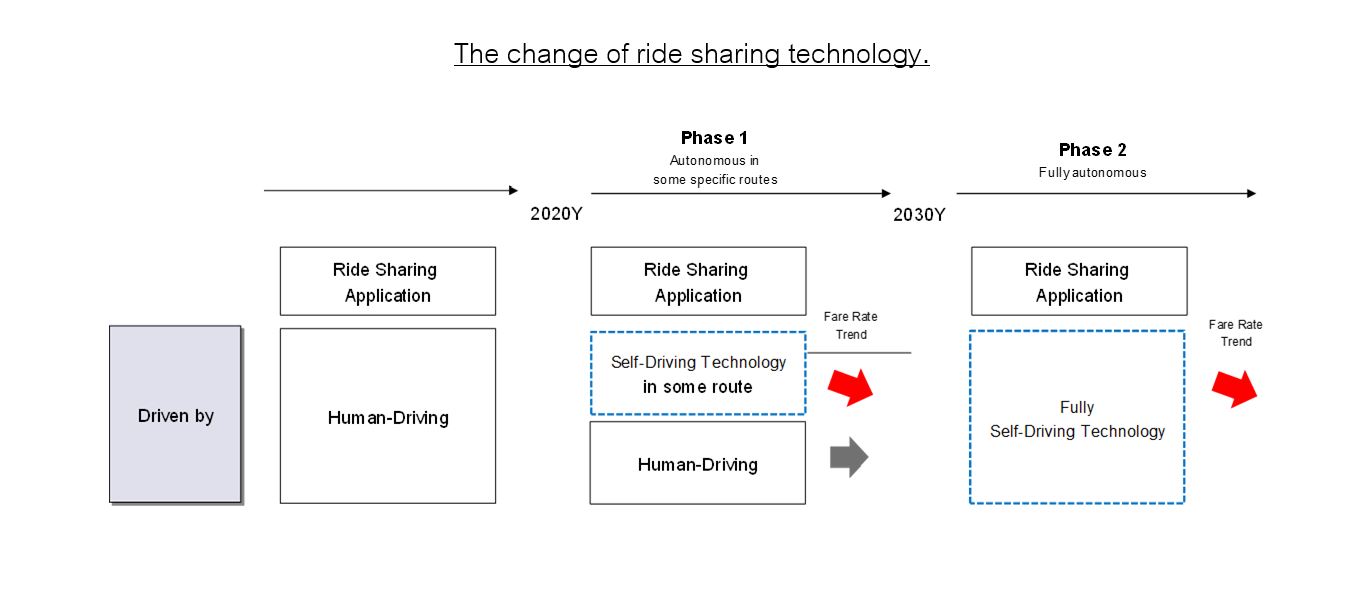
Autonomous car technology requires suitable road environment, so it is supposed to be implemented in some specific routes at the beginning as the alternative option on ride-sharing service in order to reduce manpower cost and offer a competitive price. Finally, the competitive environment will be transformed into “transformation-as-a-service” which people can request autonomous public transport anywhere anytime, by 2030 or earlier. As a result, traditional Taxi service driven by a human is expected to gradually fade out from the market since 2020.
The change of ride sharing technology
Conclusion
“Transportation-as-a -service” will be the new promising transportation mode in the future unavoidably. Automobile manufacturers including technology companies are attempting to become a part of the new value chain where mobile application has still been the center and main interface of people.
“every day super apps” of ride sharing (ride hailing) service providers is a strategy to engage people with many services while prevent giant competitors by familiar experience during the transition of technology.
Finally, ride sharing application will become “a single application” including all on demand services connecting online and offline together from transportation service both autonomous and human-driven vehicles, financial services, health care, delivery until mobile miscellany no matter how advanced the technology has been developed.
This is probably one of the major reasons why Masayoshi Son who is the broad director of Vision Fund, the largest technology fund in the world, invested in the ride sharing service providers around the world such as UBER, GRAB, OLA and DIDI CHUXING.
Reference
https://www.marsdd.com/news/ride-sharing-the-rise-of-innovative-transportation-services
http://fortune.com/longform/grab-gojek-super-apps
http://www.businessinsider.com/the-18-driverless-car-breakthroughs-2030-2016-12
https://images.app.goo.gl/TUJYy6yyQX6T4GHMA






 Download attachments
Download attachments